These animations explain what geogrid is and cover its types, why it should be used. We will first cover how it works for segmental retaining walls and then within a pavement structure.
A geogrid is a geosynthetic material that:
- Reinforces soils
- Increases gravity capabilities of SRW
- Stabilizes aggregates in pavements
- Prevents soils from pulling apart under load
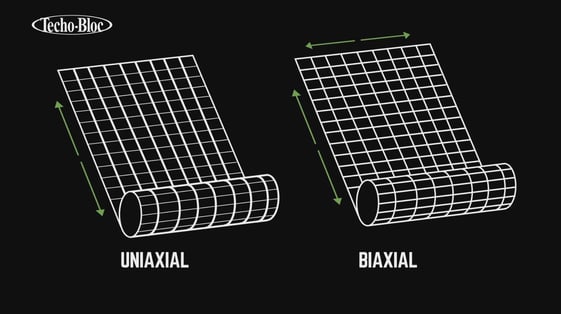
Two main types of geogrid exist on the market:
- Uniaxial
- Biaxial
A uniaxial geogrid provides strength in one direction, as opposed to a biaxial type, which has strength in both directions.
Why should you use it?
A geogrid increases bearing ability, reducing the spreading of gravel and soils.
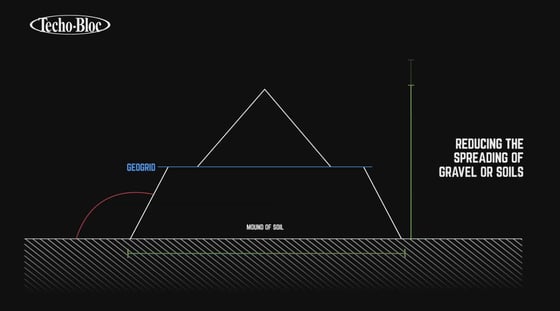
It confines and stabilizes the layers of soil.
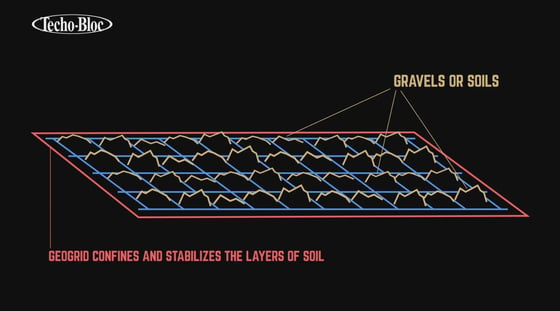
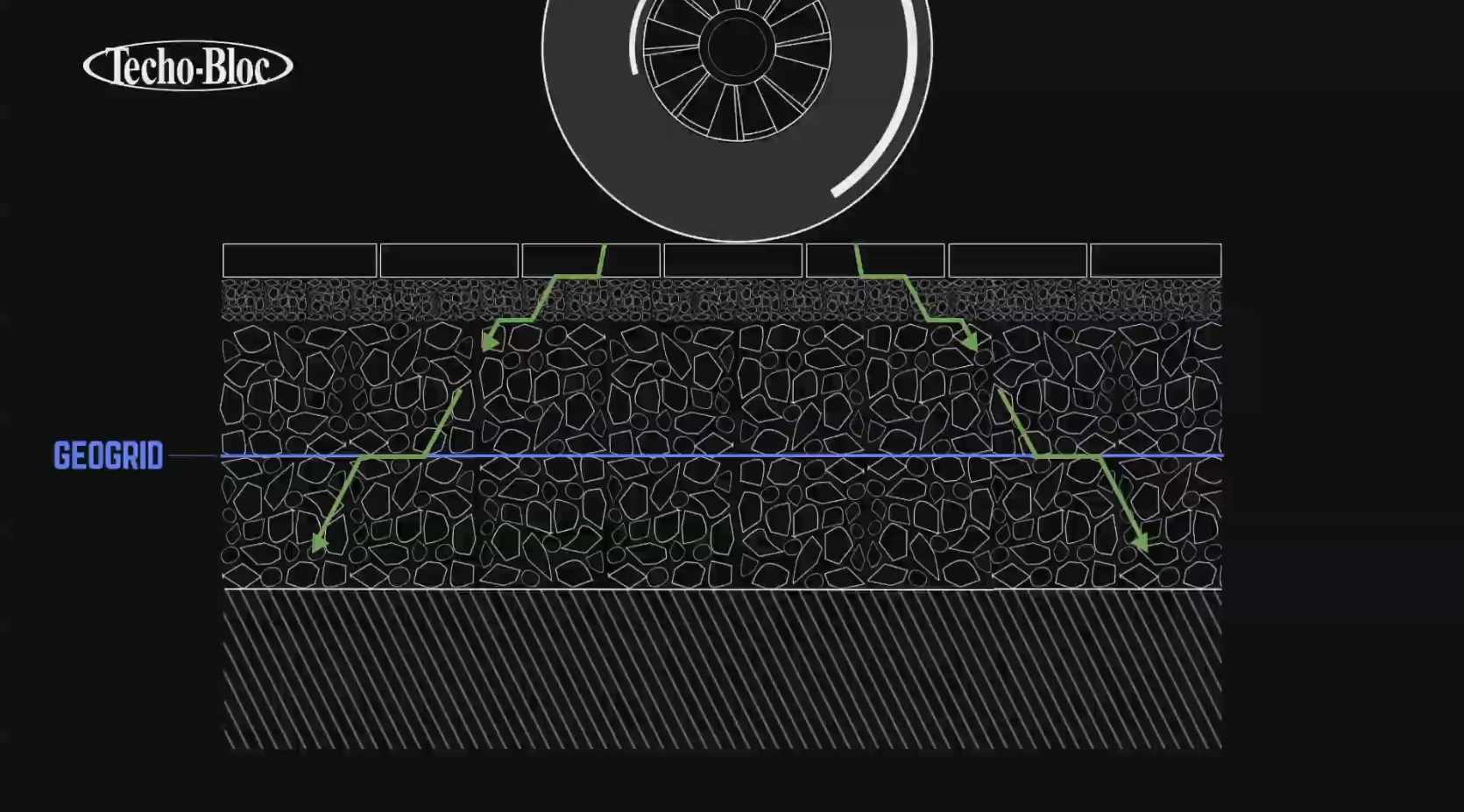
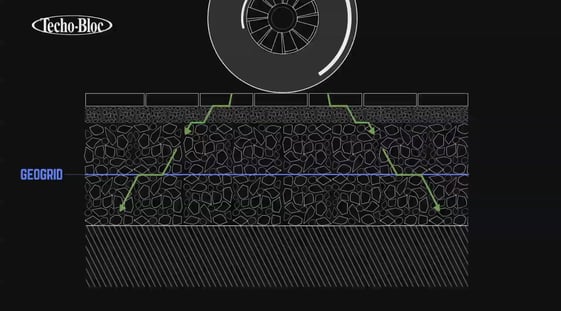
How does it work for pavement?
Adding a geogrid in a pavement application permits better load distribution in the entire system.
The weight of vehicular and pedestrian traffic is spread on a larger surface, giving more support to the structure.
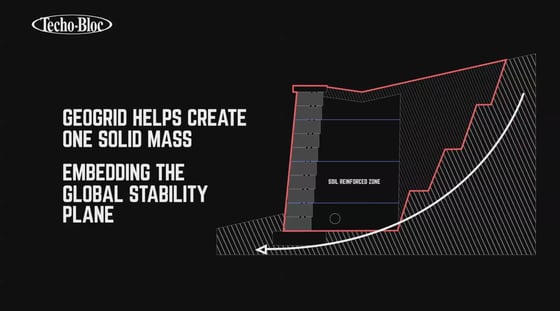
How does it work for segmental retaining walls?
A geogrid does not hold back the wall block!

It helps create one solid mass, further embedding the global stability plane.
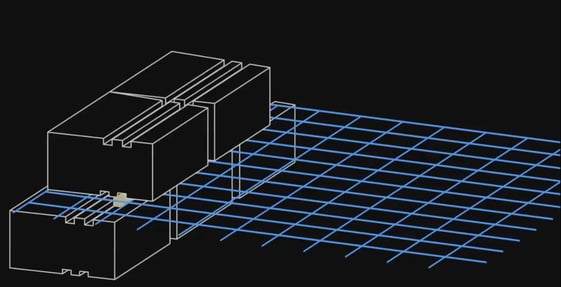
Finally, clips and block weight help tension the geogrid.
Grid should always be level and hand-taught (3% tension). It is also very important to not overlap pieces of geogrid. This reduces the friction in what is supposed to be a stabilization layer.
In the case of curved walls, or corners, where lengths of grid would have to overlap to ensure proper coverage, you are required to have at least 3" of soil (aggregates are soils too) between the layers. This could mean skipping a row of block in order to maintain the grid spacing. Learn more about this technique in the latest edition of the Techo-Spec guide.
CURIOUS ABOUT HOW GEOGRID IS INSTALLED?
CHECK OUT THIS ARTICLE!